It’s the age of the customer and the world’s biggest brands are duking it out every day for a greater share of our hearts, minds, and wallets. Customers hold more decision power than ever in an era where information about any company’s products and services is just a mobile search away.
Where does the Voice of the Customer (VoC) land in the priorities for your company’s overall strategy? Forrester’s Customer Experience Council survey shows that 79% of all respondents believe that measuring customer experience is a top priority.
Market research shows that the Customer Experience Management (CEM) market is estimated to grow from USD 5.06 Billion in 2016 to USD 13.18 Billion by 2021, at a CAGR of 21.1%.” If you’re not investing in CX, it’s very likely that your competitors are.
The stage has been set – now let’s jump right into the top Reasons to Invest More in Customer Experience (CX):
1. The ROI customer experience
Building customer loyalty and increasing revenue go hand in hand. When compared with customers who had negative experiences, those who had positive experiences were more likely to recommend, trust, try new products or services, purchase more, and forgive your company after a mistake.
2. What gets measured gets done
Measuring customer feedback is the first step to measuring up to your customers’ expectations. Whether you’re an advanced scorecard-driven enterprise or just beginning to think about CX, the most important thing to do is to start actively listening and measuring your customers’ feedback.
3. Time to set new customer experience goals
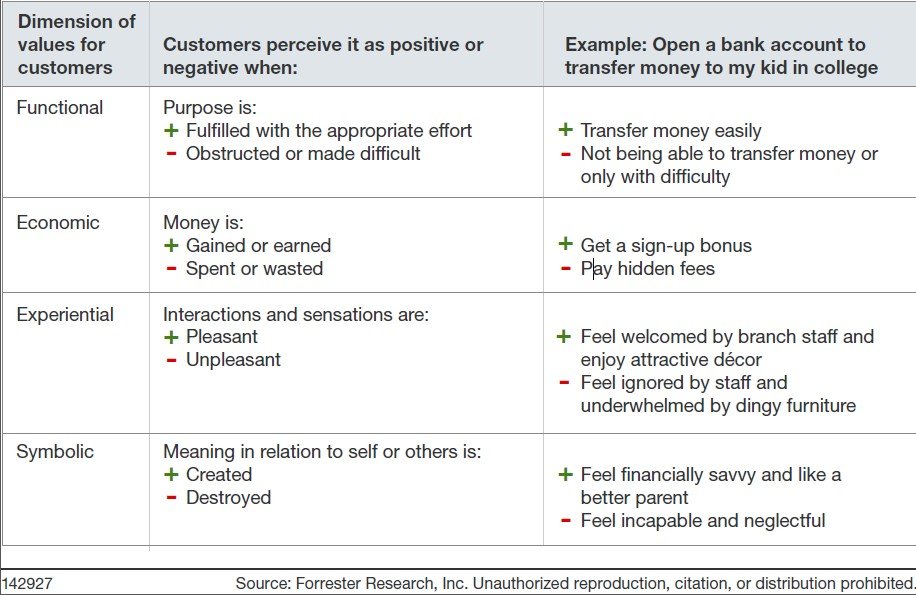
CX is not as fluffy as it may seem. There is real science and methodology to measuring and improving customer satisfaction (CSAT). There are many metrics to consider as part of your VoC program, but Bain & Company’s Net Promoter System and Forrester’s Customer Experience Index stand out as the gold standard top-line measures in the CX industry.
4. Elevate your operational performance
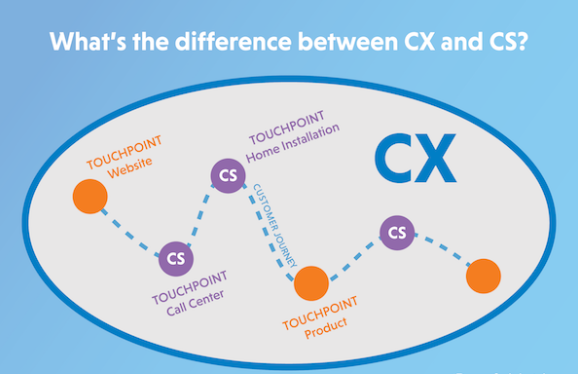
Operational performance and CSAT are inextricably linked. For example, it’s no coincidence that airlines with the best CX ratings also boast the highest percentage of on-time arrivals. The best CEM programs cause cross-functional customer-centric collaboration, which requires your company to break down organizational silos to be more valuable, efficient, and enjoyable to your customers.
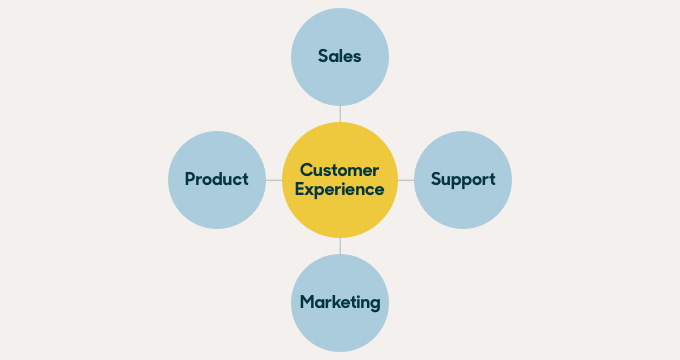
5. Put the customer at the center of every decision
Your customers see you as one whole cohesive brand, regardless of how complex your organization, systems, and processes might be. When your customer interacts with your company, they don’t care about any bureaucracy, different divisions and departments, or roles and hierarchies.
6. Plug-in and empower your employees
Ready to take your CX program to the next level? Tap into your company’s most valuable assets – your people. The more customer-facing employees with access to a real-time view of customer feedback, the more awareness, focus, and unity there is around your company’s CX mission and goals.